Written by Jonathan Trinque, Research Services Coordinator, UConn Archives & Special Collections
The UConn Library’s Archives & Special Collections holds over 1000 archival collections. Some of these collections are well known and are used all the time for research, while others may not have been accessed since they arrived at the archives. Because of this, I thought it would be fun to spotlight some collections that I have come across that seem interesting, and that researchers have not used much or simply do not know that they exist.
Here are some other collections that I have come across that piqued my interest. I hope you find them as interesting as I do, and maybe reading about them will spark your next research project!
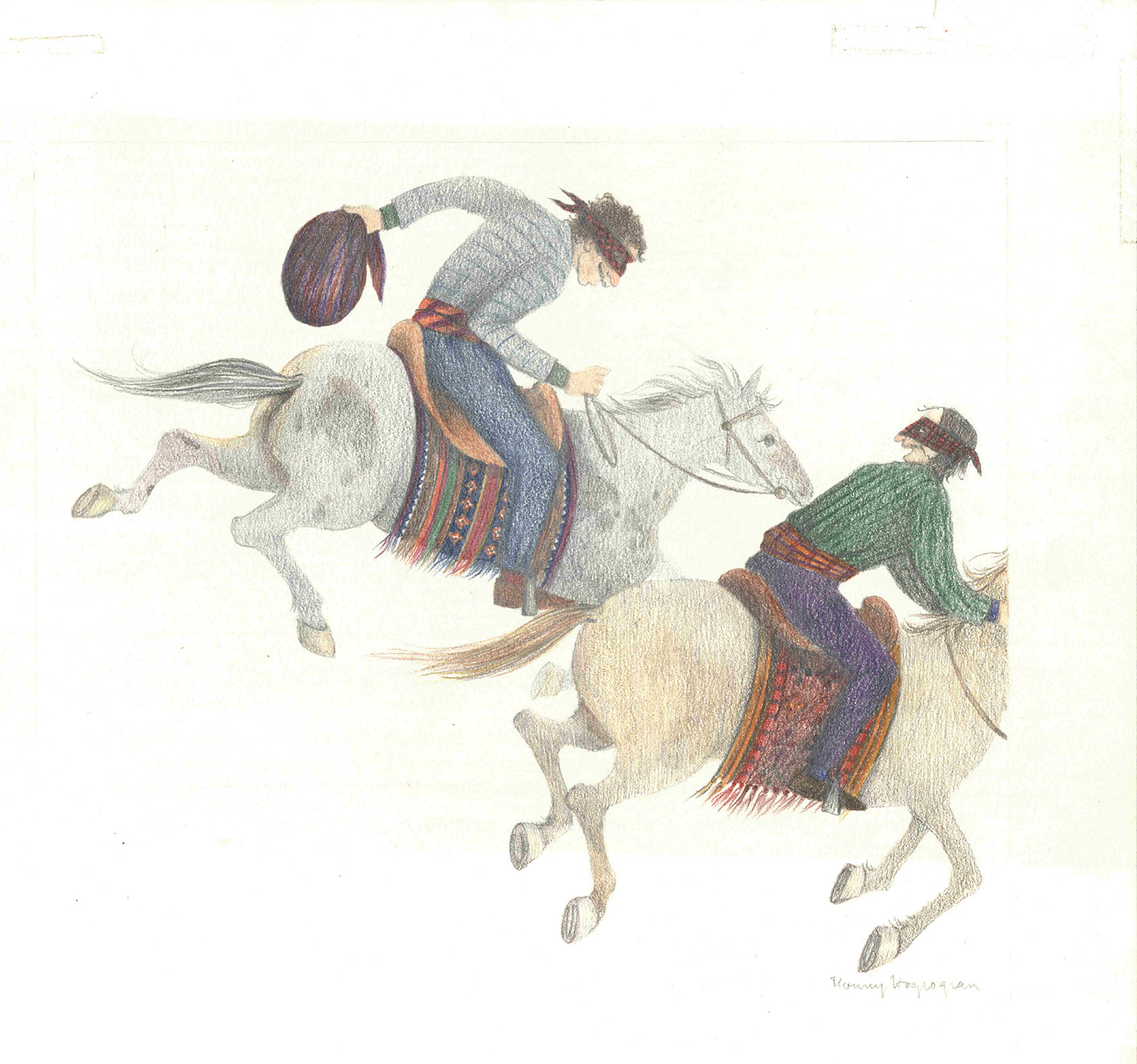

Nonny Hogrogrian was a critically acclaimed Armenian American author, illustrator, and designer of children’s literature.
Hogrogian grew up in an artistic family; her parents were amateur painters, and her sister went on to become an interior designer. Hogrogian began painting at a very young age. She always had a love for folktales and fantasy, as well as poetry, which is clearly shown in her body of work. Hogrogian is known for intricate illustrations and attention to detail that capture the personalities of her various characters. She has also been attributed to bringing multiculturalism into children’s literature by incorporating her Armenian heritage into her books.
Hogrogian studied fine art at Hunter College, earning herself a B.F.A in 1953. She freelanced as a book-jacket designer for William Morrow after graduation. Hogrogian continued her studies at The New School for Social Research where she studied life drawing. While at the New School, Hogrogian learned the art of woodcutting from Antoni Frasconi. Shortly after graduating from her master’s program in 1957, Hogrogian became a production assistant at Thomas Y. Crowell Co. in 1958. At Crowell, she illustrated her first published children’s book, King of the Kerry Fair. Hogrogian eventually moved on to work for Holt & Co. as an art director. Her work at Holt earned her first Caldecott Medal in 1966 for her work with Leclaire G. Alger (also known by the pen name, Sorche Nic Leodhas) on Always Room for One More. Hogrogrian won another Caldecott in 1972 for her self-illustrated book One Fine Day, and a Caldecott Honor Award in 1977 for The Contest, a retelling of an Armenian folktale.
I wanted to spotlight this collection because Nonny’s work is extraordinary but is often overshadowed by other big names that she has collaborated with. I resonate with her love of folktales and fairytales, and the beautiful illustrations that often accompany such stories. I also found her background and how she charted her career through various educational institutions and jobs in the publishing industry to be important and inspiring for early career professionals in children’s literature trying to break into the industry.
I strongly recommend experiencing Nonny Hogrogian’s collection in-person in our reading room and giving this underutilized collection the attention it deserves.
Related Resources:
Nonny Hogrogian Papers | UConn Archives & Special Collections
David Kherdian Papers | UConn Archives & Special Collections

Michael Rumaker was an American author known for his semi-autobiographical novels that document his life as a gay man from his early life in the 1950s to his death in the 2010s.
Rumaker was born in South Philadelphia and grew up in a small town in New Jersey. He went on to attend Rider College in Trenton where he majored in journalism, but after hearing Ben Shahn’s enthusiastic praise of Black Mountain College, he applied and was accepted.
Rumaker was granted a work scholarship where he worked seven days a week in Black Mountain’s kitchens. During his time at Black Mountain College, Rumaker studied writing under the tutelage of Charles Olson and Robert Creeley. Rumaker’s breakthrough work was his short story “The Truck.” He originally wrote in one of Olson’s writing classes in 1954 and sent it to Robert Creeley to be published in the Black Mountain Review. This was a very encouraging experience for Rumaker that led to his writing of three additional stories during his winter break that followed, including “Exit 3” and “The Pipe,” both of which were eventually published.
In 1955, Rumaker graduated from Black Mountain with an honors degree with Robert Duncan as his outside examiner. He was one of very few students to have graduated during the college’s final years. After graduation, Rumaker worked various jobs during the day and worked on his writings at night. He worked in Philadelphia at an advertising agency. He eventually quit and hitchhiked all the way to San Francisco where he found work as a clerk for a steamship company. He continued writing in his spare time and stayed with friends from Black Mountain. From then on, his life continued to intersect with other artists from the Beat Generation.
There is still much more to Michael Rumaker’s interesting life and career that I could not include in this already-too-long blog post. I really wanted to spotlight his collection and published works as I feel together they really capture the life of someone who was a writer and creative to his very core and was so deeply dedicated to his craft. Reading about how hard he worked for his education, going from a kid in a small town to being a well-regarded published author, was inspiring and encouraging.
There is so much untapped research potential in this extensive collection, and if my enthusiastic review of it has not persuaded you to check it out, maybe George Butterick’s words will finally sell you on it.
According to George Butterick, who began reading and collecting Michael Rumaker’s literary papers at the University of Connecticut in 1974, “Rumaker has proceeded from writing about disengaged youth in a generation willing to declare its difference, to being a celebrant of total life and human joy. Actively participating in his own destiny, he has left a glowing trail of work to document the struggle toward identity. He represents, in his later writings, one extension of the Beat revolution: the embracing of sexual diversity. Governing all his work is an indefatigable spirit that gives the creative life reward.”
Related Resources:
Michael Rumaker Papers | UConn Archives & Special Collections ArchivesSpace
BMC Yearbook Biographies | Michael Rumaker

This small but important collection features correspondence from Michael Rumaker to his long-time friend and former partner, Merrill Gillespie, documenting the pair’s early relationship in the mid-1950s while they both attended Black Mountain College.
Gillespie was born in Kewanee, Illinois and attended Black Mountain College from Spring 1949 – Fall 1952 pursuing his studies in music composition. He attended with composer David Tudor, artist Herb Roco, poet Marie Tavroges Stilkind, and of course Michael Rumaker. At an early age, Gillespie contracted an ear infection that made him hard of hearing for most of life. Despite this, he followed his passion for music studying under Lou Harrison during his Black Mountain College years, and David Garner during the last 25 years of his life. Over the course of his life he composed many works including several chamber works and three orchestral works.
I wanted to draw attention to this small collection because it complements Michael Rumaker’s collection and is easy to overlook. I think through the letters included in this collection you can really get a sense of each of them as individuals, their relationship with one another, and what their lives were like while attending Black Mountain College. I think these collections work together to accomplish one of the main goals of an archive; to give the fullest picture possible of an individual, the life they lived, and the context in which they existed.
Related Resources:
Merrill Gillespie Papers | UConn Archives & Special Collections ArchivesSpace
BMC Yearbook Biographies | Merrill Gillespie
Merrill Gillespie Obituary | 1931 – 2017 | Daly City, CA
If any of these collections have piqued your interest, you are always welcome and encouraged to view them in-person in our reading room or by accessing them remotely through reproductions. To learn more about how to access our collections, please visit our website: https://s.uconn.edu/asc
Citations:
Photograph of Michael Rumaker in Sausalito, 1956. Photograph by Jonathan Williams. Western Regional Archives, Asheville, North Carolina. Retrieved on February 17, 2026. https://bmcyearbook.org/bio/michael-rumaker
Photograph of Merrill Gillespie included with student application. Western Regional Archives, Asheville, North Carolina. Retrieved on February 17, 2026. https://bmcyearbook.org/bio/merrill-gillespie
Original Artwork from Nonny Hogrogian’s The Contest (1976). Nonny Hogrogian Papers, Box 1, University of Connecticut Library, Archives & Special Collections